Infographics
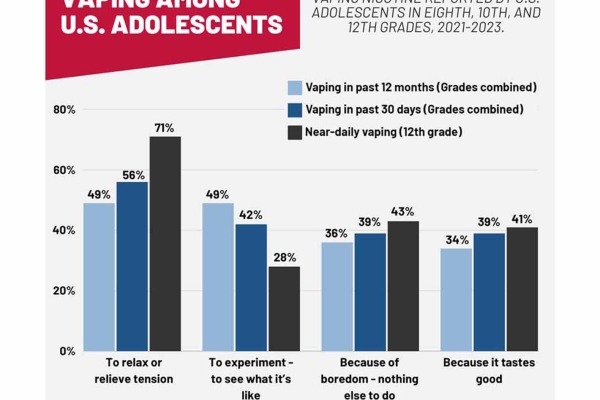
Reported Reasons for Vaping Among U.S. Adolescents (2021-2023)
|
US adolescents who vaped nicotine reported a wide range of reasons for the behavior, according to a NIDA-supported study published in Pediatrics.
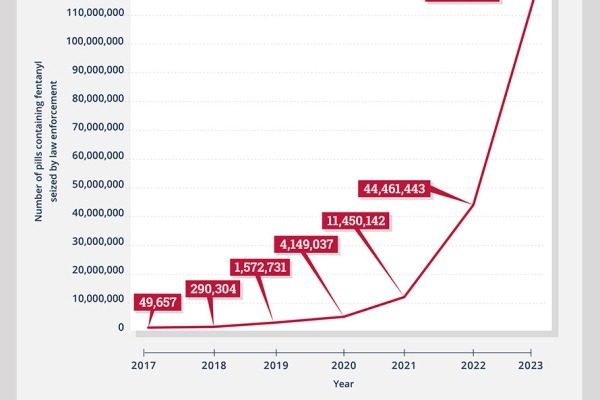
Number of Pills Containing Fentanyl Seized by Law Enforcement in the United States, 2017-2023
| En español
|
NIH-supported study highlights increasingly dangerous illicit drug supply, risk of pills not coming from a pharmacy
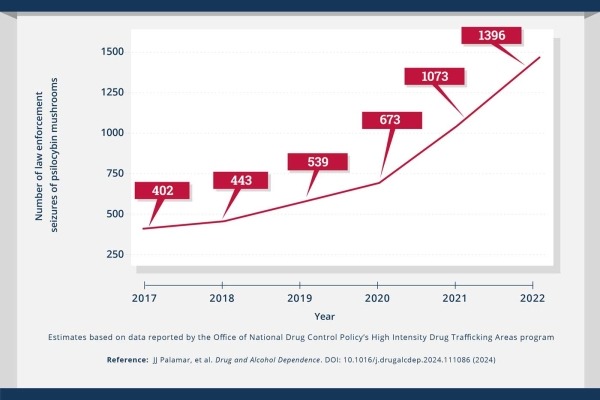
Law enforcement seizures of psilocybin mushrooms rose dramatically between 2017-2022 (Infographic)
| En español
|
NIH-supported research highlights need to better understand psilocybin in context of growing psychedelic use
|
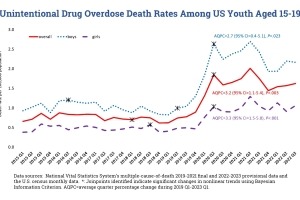
Quarterly rates of unintentional drug overdose deaths among teens 15-19 remained elevated well into 2022.
|
Explore the different types of medications prescribed for opioid overdose, withdrawal, and addiction. Medications for overdose of opioids, withdrawal, and addiction are safe, effective, and save lives. This Medications for Opioid Use Disorder (MOUD) Infographic helps present basic information on common medications and formulations available to consumers.
|
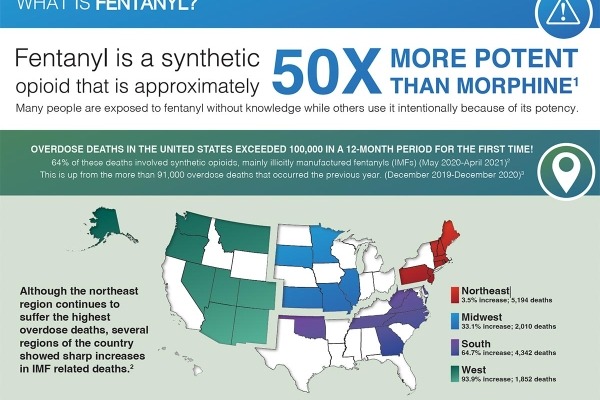
Fentanyl is a synthetic opioid that is approximately 50 times more potent than morphine
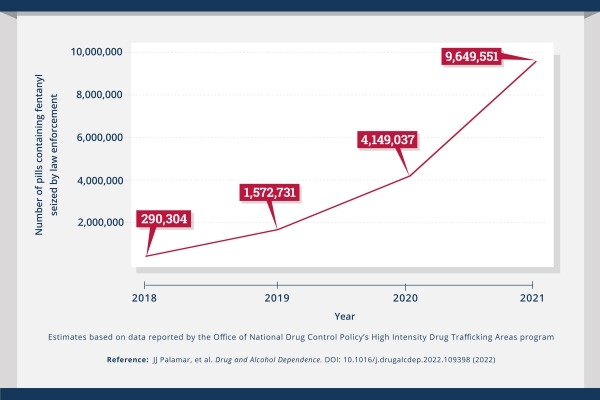
Number of Pills Containing Fentanyl Seized by Law Enforcement in The United States, 2018 -2021
|
This graph highlights growing, dangerous trend, particularly for people new to drug use
|
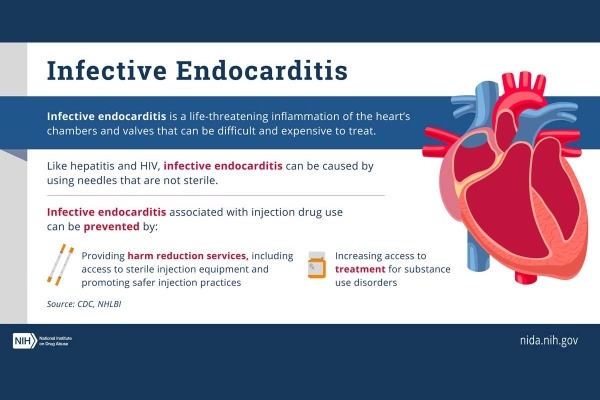
Highlights basic information about infective endocarditis alongside an anatomical image of a human heart
|
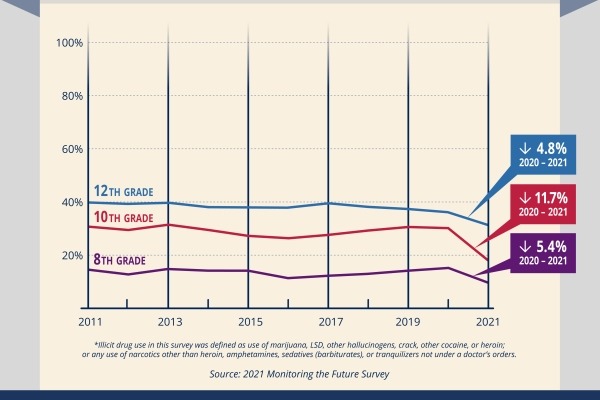
The percentage of adolescents reporting substance use decreased significantly in 2021
|
Driving while under the influence of legal or illegal substances puts the driver, passengers, and others who share the road in danger.